OverviewBizagi provides two different conditional shapes: Conditional activity and Conditional event. The Conditional activity is an extension to the. Both shapes are available to be used for execution, especially when working with unstructured processes.Conditional activities are enabled or disabled during the course of a case instance depending upon a business condition. They represent a user task that when enabled are allocated to an end user.A condition must be set to the Conditional activity to enable or disable it, according to the business requirements. In Runtime, allocated end users will be able to see the task in their pending lists when the condition is met. If the condition is not met, the task disappears from the Inbox, like it never existed.Conditional activities do not need incoming paths. If they do not have an incoming path they will be available as soon as the processes containing it is created, and will be listening to the data, waiting for the condition to be met, to be enabled.
If they do have an incoming sequence flow, the task will start listening to be enabled when a token arrives.Conditional events are enabled as soon as a token arrives to them, but will wait until a condition is met to move on to the next step in the process flow. They do not have a user interface, that is, they are not allocated or available for end users. These shapes are not disabled, unlike Conditional tasks. It is mandatory for a Conditional Event to have an incoming path since the event condition starts to be evaluated as soon as a token arrives to the event.NOTES:.Since conditional activities do not need an incoming sequence flow they cannot have On Enter actions.Conditional activities with no condition defined will behave like regular user activities.When configuring Conditional activities and Conditional events, make sure that every attribute used in their condition is initialized in the process. Otherwise, the operation involved will result in an error when evaluating true or false against a null value.The conditions are triggered when there is an actual change in the attributes being evaluated (i.e. VIP customer changing from true to false).
Tem Como Estimar O Mfv Atraves Do Bizagi A Pdf
Thus, static attributes will not trigger an event (i.e. When Date A is greater than Date B, since these date are not actually changing).Imagine an Emergency Room.
Tem Como Estimar O Mfv Atraves Do Bizagi Free
A Patient arrives and a triage is performed. Then, a doctor examines the patient and usually some exams are ordered. Only when all the exams are taken and a result for all of them is received, should the Review exams activity be enabled. Thus, the Review exams task is represented using a Conditional Task. This way, when Bizagi evaluates the condition that all ordered exams are ready, a doctor can call-in the Patient.Example of a Conditional activityConsider a scenario where a pregnant patient schedules an appointment.

These appointments can be scheduled at any time during pregnancy, so it is possible for the patient to reach the 27th week during a check out process. If this scenario becomes real during the process, a new activity is triggered. This activity will be in charge of managing the information of the patient preparation for her baby's birth.In the forth step of the wizard, create a Business Rule to define when should the activity Prepare your baby's birth be started. Select the activity to open the Expression manager window.Set a condition where the pregnancy weeks attribute of the patient is greater than 27. This way, the activity will start as soon as the number of weeks pregnant exceeds 27.Example of a Conditional eventConsider a purchase request process which can be canceled any time until the order has been quoted. Once quoted the request cannot be canceled.As the process is created the conditional event receives a token, and thus is enabled and listening to the process data to be executed.In this case the event will be waiting for one of two options: First, the process arrives the state of no longer cancel-able or second, the process is manually canceled.
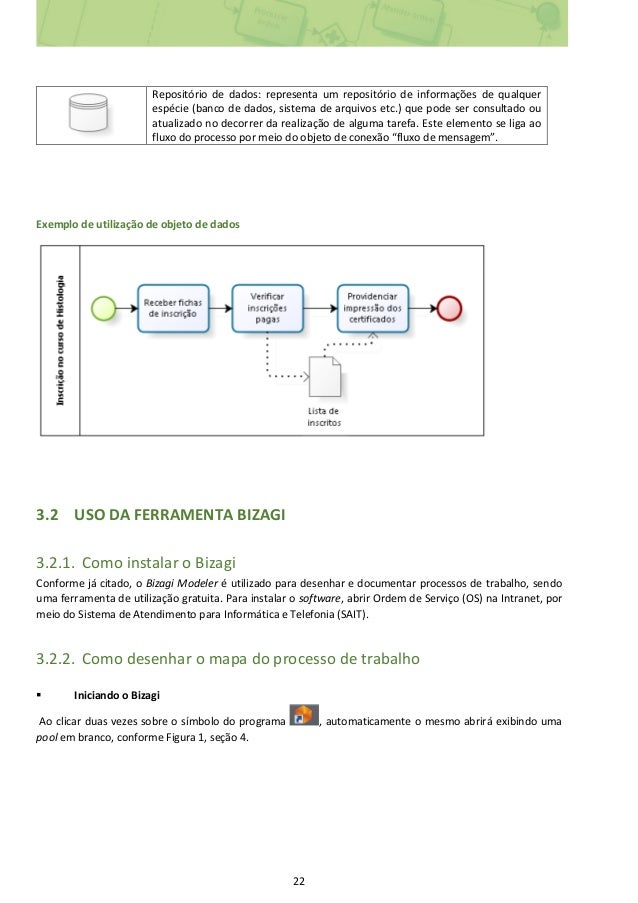
If any of the two options is met, the event will move forward, evaluating a gateway to identify if the process must close or not.This behavior is managed through two Boolean parameters, Is Cancellable (to execute the event and thus disable it as soon as the process arrives to the Quote milestone) and Is Canceled (if an Action sets the Canceled attribute before the Quote milestone, it executes the event to finish the process).The following image displays the condition of the event.